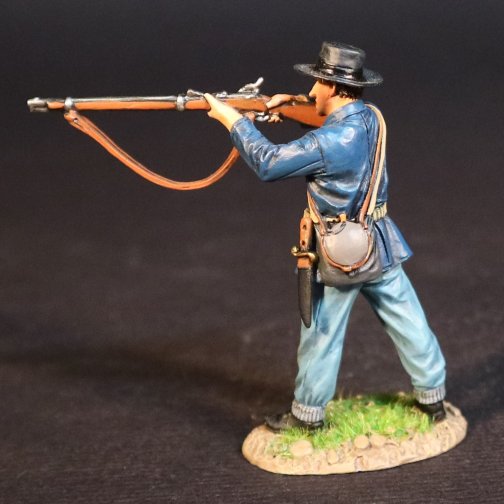
RSBUD-14 United States Mounted Infantry, Battle of the Rosebud
$49.00
Description
On 28th May 1876, Brigadier General George Crook assumed direct command of the Bighorn and Yellowstone Expedition at Fort Fetterman. Crook had gathered a strong force. Leaving Fort Fetterman on 29th May the 1,051 man column consisted of 15 companies from the 2nd and 3rd Cavalry, 5 companies from the 4th and 9th Infantry, 250 mules and 106 wagons. On the 14th June, the column was joined by 261 Shoshone and Crow allies.
Based on intelligence reports Crook ordered his entire force to prepare for a quick march. Each man was to carry only 1 blanket, 100 rounds of ammunition, and 4 days rations. The wagon train would be left at Goose Creek, and the infantry would be mounted on the pack mules.
On 17 June, Crook’s column set out at 0600, marching northward along the south fork of Rosebud Creek. The Crow and Shoshone scouts were particularly apprehensive. Although the column had not yet encountered any sign of Indians, the scouts seemed to sense their presence. The soldiers, particularly the mule-riding infantry, seemed fatigued from the early start and the previous day’s 35-mile (56 km) march. Accordingly, Crook stopped to rest his men and animals at 0800. Although he was deep in hostile territory, Crook made no special dispositions for defense. His troops halted in their marching order. The Cavalry battalions led the column, followed by the battalion of mule-borne foot soldiers, and a provisional company of civilian miners and packers brought up the rear.
The Crow and Shoshone scouts remained alert while the soldiers rested. Several minutes later, the soldiers heard the sound of intermittent gunfire coming from the bluffs to the north. As the intensity of fire increased, a scout rushed into the camp shouting, “Lakota, Lakota!” The Battle of the Rosebud had started. By 0830, the Sioux and Cheyenne had hotly engaged Crook’s Indian allies on the high ground north of the main body. Heavily outnumbered, the Crow and Shoshone scouts fell back toward the camp, but their fighting withdrawal gave Crook time to deploy his forces. Rapidly firing soldiers drove off the attackers but used up much of the ammunition meant for use later in the campaign. Low on ammunition and with numerous wounded, the General returned to his post.
Historians debate whether Crook’s pressing on could have prevented the killing of the five companies of the 7th Cavalry Regiment led by George Armstrong Custer at the Battle of the Little Bighorn.
The Sioux troubles increased the need for mounted troops on the frontier, and as early as December 6th 1866, elements of the 18th Infantry were mounted, and operating alongside Cavalry. The practice of using mounted infantry continued until the end of the Indian wars.